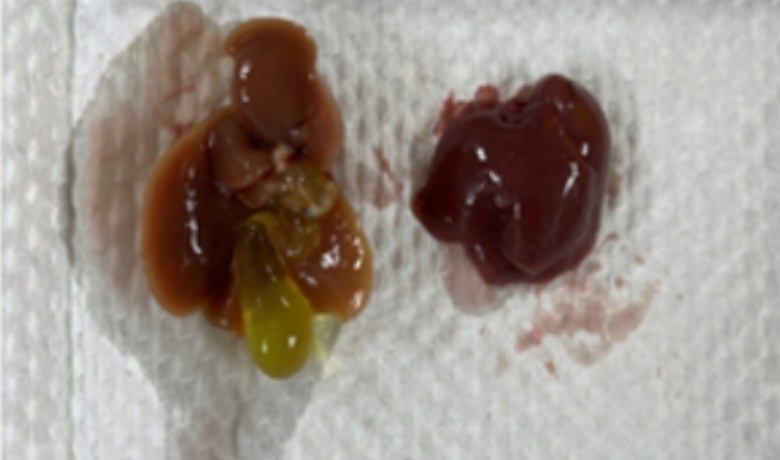
hepatic fibrosis model
Hepatic fibrosis is the common pathological basis for the development of cirrhosis in a variety of chronic liver diseases. Although the study of liver fibrosis has entered the molecular level from the cellular level, the establishment of liver fibrosis animal model is still the focus and difficulty of clinical research and experimental research. The establishment of animal models of liver fibrosis can not only study the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis in depth and comprehensively, but also provide a research basis for clinical research on drugs for the prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis.
Technical principle
Liver fibrosis is the main pathological basis for the development of many chronic liver diseases to cirrhosis. Although the study of liver fibrosis has developed from the cellular level to the molecular level, the establishment of liver fibrosis animal model is still the focus and difficulty of clinical and experimental research. Through the establishment of liver fibrosis animal model, we can deeply and comprehensively study the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis, and provide basic research for clinical screening of drugs for the prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis. At present, animal models of liver fibrosis can be divided into gene-related models and non-gene models. Gene-related models mainly refer to engineered animal models, while non-gene models mainly refer to liver fibrosis models induced by environmental factors, drugs/poisons or other factors under the same or similar genetic background. Common animal models of liver fibrosis include chemical agent induction methods (e. g., carbon tetrachloride induction, thioacetamide induction), bile duct obstruction methods (e. g., bile duct ligation or parasite methods), ethanol induction methods, and immunization methods.
Real Experimental Research Hundreds of Detection Experiments 6 Experimental Platforms