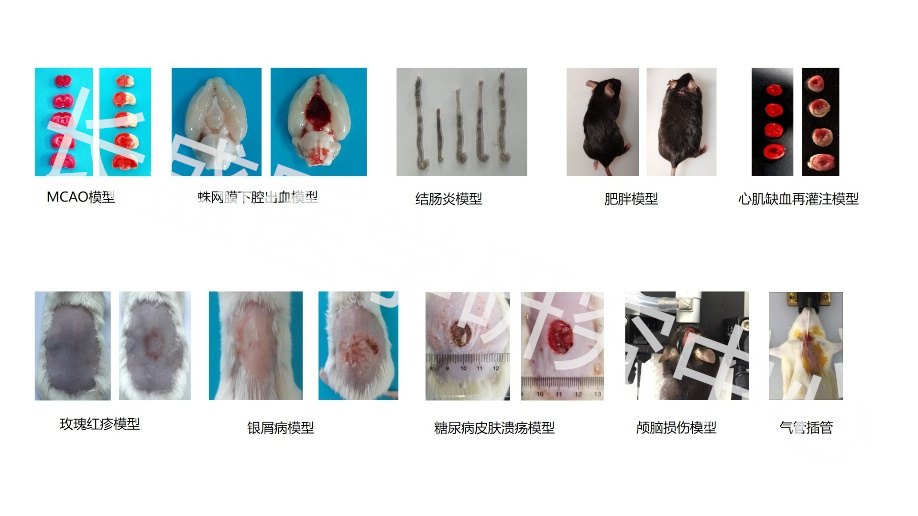
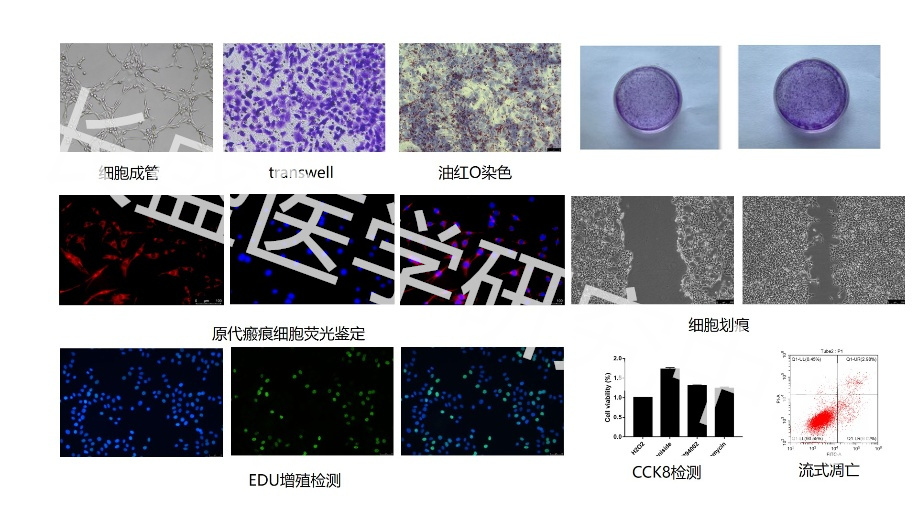
clone formation
The clone formation rate and cell clone seeding survival rate were calculated by observing the formation of single cell colonies to evaluate the proliferation ability of the cells. When a single cell continues to proliferate for 6 passages or more in vitro, the number of cells has reached about 60. This cell population is called a clone or colony, and its size is between 1.0-2.0mm. The colony formation rate indicates the independent viability of the cells, and different physicochemical factors may change the clonogenic ability of the cells. By counting the colony formation rate, the proliferation potential of a single cell can be quantitatively analyzed, and then its proliferation rate and adaptability to the living environment can be understood. Commonly used methods include soft agar culture and plate cloning.
Technical principle
The colony formation rate and cell clone seeding survival rate were calculated by observing the formation of single cell colonies, thereby evaluating the proliferation ability of the cells. When a single cell continues to proliferate for 6 passages or more in vitro, the number of cells has reached about 60. This cell population is called a clone or colony, and its size is between 1.0-2.0mm. The colony formation rate indicates the independent viability of the cells, and different physicochemical factors may change the clonogenic ability of the cells. By counting the colony formation rate, the proliferation potential of a single cell can be quantitatively analyzed, and then its proliferation rate and adaptability to the living environment can be understood. Common methods include soft agar culture or plate cloning.
Real Experimental Research Hundreds of Detection Experiments 6 Experimental Platforms