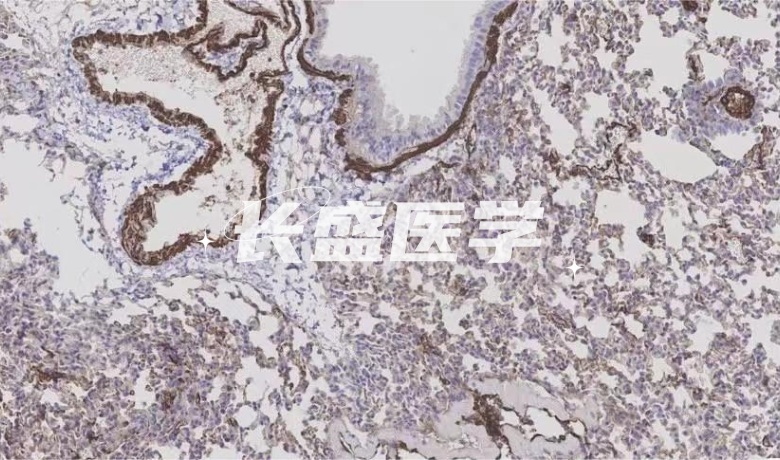
IHC staining/immunohistochemistry
Antigen-antibody reaction is an important experimental technique, which is achieved by the specific binding between antigen and antibody. In this process, we use a chemical reaction to make the chromogenic reagent of the labeled antibody (such as luciferin, enzyme, metal ion, isotope) color reaction, and then determine the antigen (including polypeptide and protein) in the tissue cells. Through this technology, we are able to accurately locate, characterize and relatively quantify antigens within cells. This technology has a wide range of applications in biological research and provides a powerful tool for scientists to explore the function and interaction of molecules inside cells.
Technical principle
Antigen-antibody reaction is a special chemical binding principle. Through the specific interaction between antigen and antibody, the location, nature and relative quantity of antigen are determined in tissue cells. Through clever chemical reaction, the antibody can be labeled with chromogenic agents (such as luciferin, enzyme, metal ion, isotope), and the color effect can be produced, so as to realize the visualization of antigen. This method is a widely used technology in the field of biology. It can not only help us understand the polypeptide and protein antigens in the cell, but also accurately locate, qualitatively and relatively quantitatively analyze them. Through a clear, precise and engaging creative approach, we can gain a deeper understanding of the importance and application of this principle.
Real Experimental Research Hundreds of Detection Experiments 6 Experimental Platforms