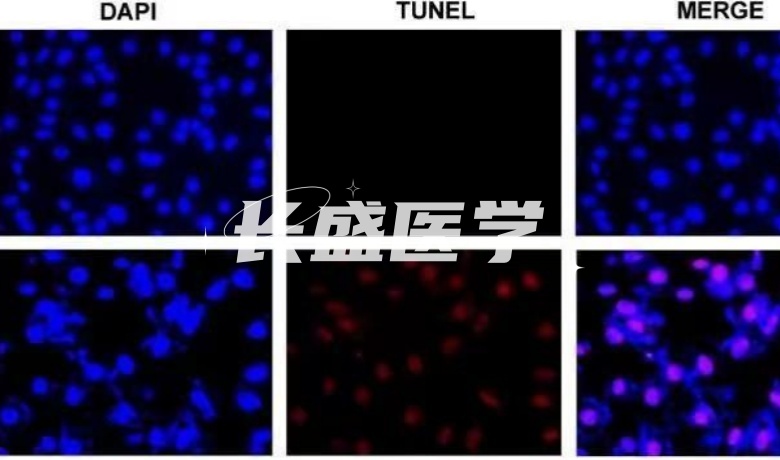
Tunel staining
When genomic DNA is broken, the terminal 3 '-OH is exposed, and these exposed ends can be catalyzed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase, TdT), allowing fluorescein-labeled dUTP (fluorescein-dUTP) to bind to it. This process can be detected using the TUNEL(TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling) method. The presence or absence of apoptosis can be easily detected by fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry.
Technical principle
When a cell undergoes an apoptotic process, it initiates the activation of certain endonucleases that cleave the genomic DNA between nucleosomes. For electrophoresis experiments for apoptosis detection, the extracted DNA showed a DNA gradient consisting of 180 to 200 base pairs. When genomic DNA splits, the terminal 3 '-OH is added to a dUTP with a fluorescein or biotin tag by a catalyst called deoxynucleotide terminal transferase (Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase, TdT). By means of fluorescence microscopy or chemical staining methods, we are able to detect cases of apoptosis.
Real Experimental Research Hundreds of Detection Experiments 6 Experimental Platforms