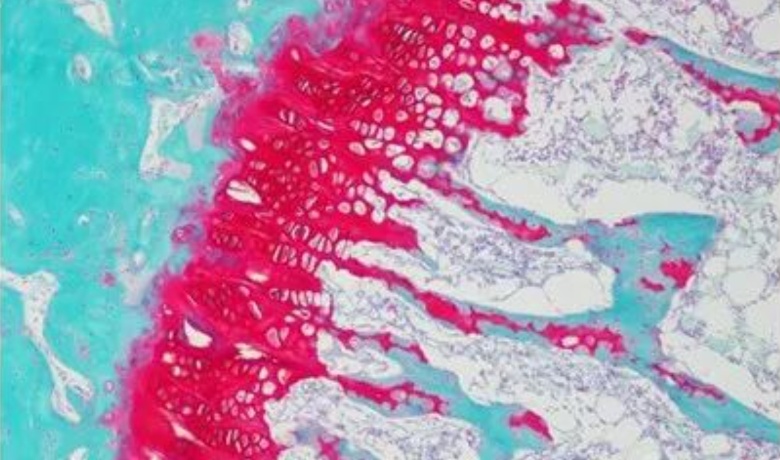
safranin solid green dyeing
Safranin is a basic dye that can efficiently display lignified, corialized and keratinized tissues of vascular plants. Fushin is an acid dye that contains plasmatic cellulose tissue and is therefore also widely used in staining studies. Some cell structures, such as ducts, can be clearly displayed by safranin staining, while sieve tubes are suitable for fast green staining. Different staining methods can help us understand the tissue structure of plants more deeply.
Technical principle
Safranin is an alkaline dye, which is widely used in the biological field. It can effectively display the lignified, corked and keratinized tissues in vascular plants. The solid green is an acid dye, in the cellulose cell tissue to play the role of staining, and contains a certain amount of pulp. By using safranin dye, we were able to dramatically highlight the ductal tissue in the vascular bundle. As an important part of vascular plants, the conduit is responsible for the transmission of water and nutrients. The selective staining of safranin allows the conduits to be more clearly displayed, further helping us to understand the water and nutrient cycling processes in plants. Unlike safranin, the solid green dye is suitable for dyeing screen tubes. Sieve tube is a kind of cell tissue with special structure, which plays an important role in material transportation and nutrient distribution in plants. By applying the solid green dye, we can effectively dye the sieve tube tissue to make it more clearly visible under the microscope, thus promoting the study of the structure and function of the sieve tube. As described above, the safranin dye and the solid green dye each play an important function in the biological field. They provide a powerful tool for us to understand the tissue structure and function of vascular plants through different staining characteristics and selective effects.
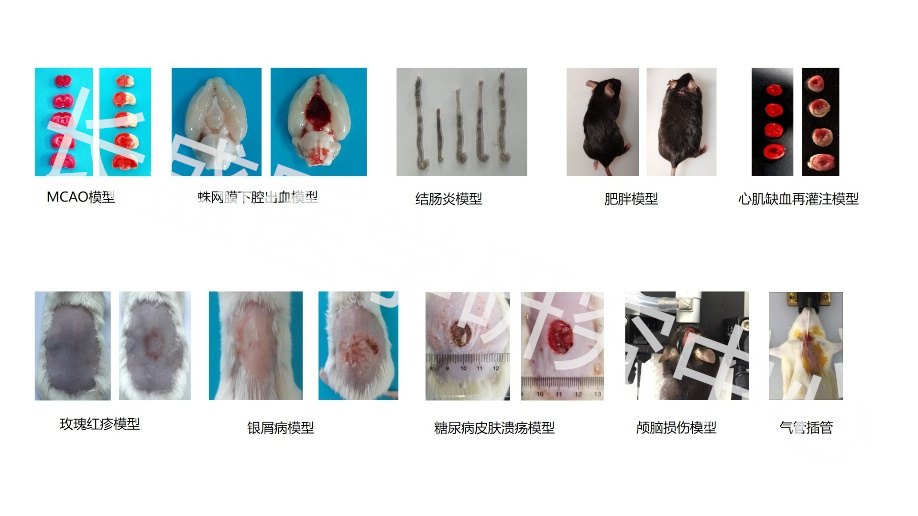
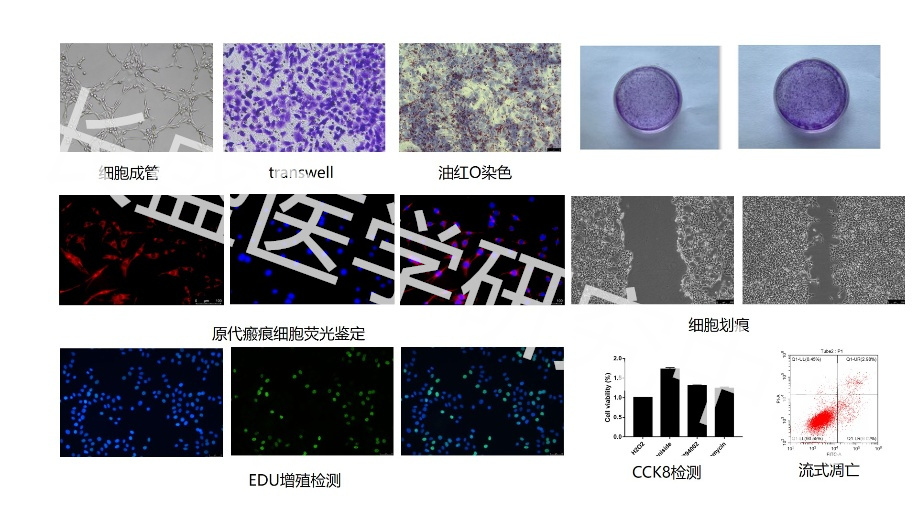
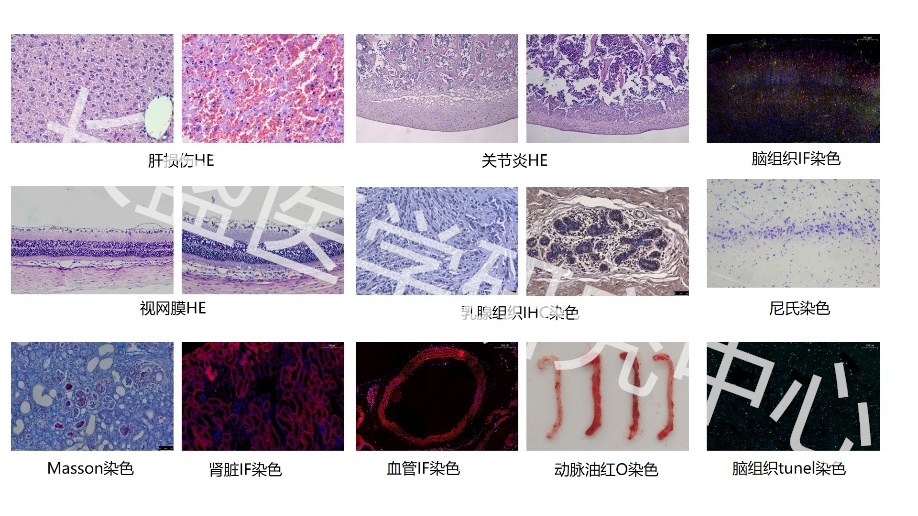
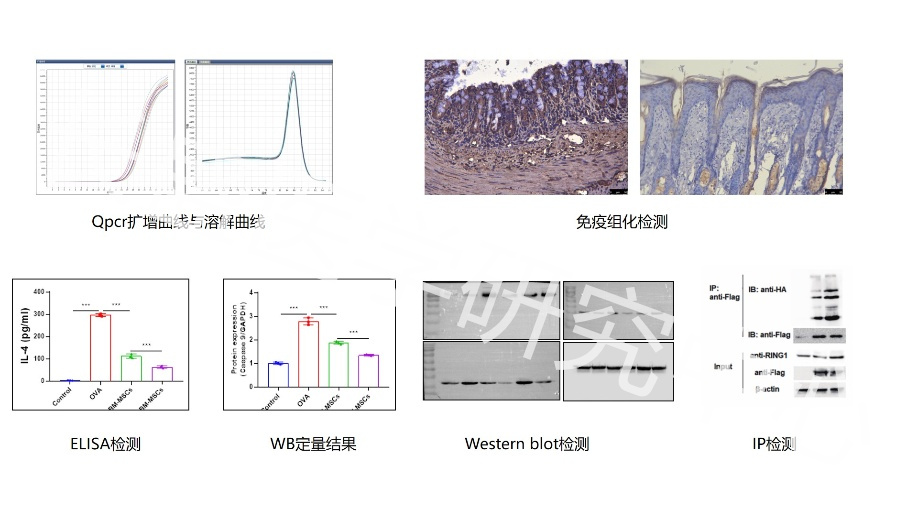
Real Experimental Research Hundreds of Detection Experiments 6 Experimental Platforms